Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Acessos
Acessos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
Motricidade
versão impressa ISSN 1646-107X
Motri. vol.11 no.1 Ribeira de Pena mar. 2015
https://doi.org/10.6063/motricidade.3441
ARTIGO ORIGINAL
Visual conditions and postural directions affect postural sway variability in patients with Parkinsons disease
Alterações nas condições visuais pode afetar a variabilidade de oscilação postural em pacientes com Parkinson em diferentes níveis da doença
Natalia Madalena Rinaldi1*, Fabio Augusto Barbieri2, Claudia Teixeira-Arroyo2, Florindo Stella2,3, Lilian Teresa Bucken Gobbi2
1Universidade de São Paulo - USP, Faculdade
de Medicina, Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brasil.
2Universidade Estadual Paulista - UNESP,
Laboratório de Estudos de Locomoção e Postura (LEPLO), Rio Claro, SP, Brasil.
3Universidade Estadual de Campinas - UNICAMP,
Campinas, SP, Brasil.
ABSTRACT
Postural sway variability was evaluated in Parkinsons disease (PD) patients at different stages of disease. Twenty PD patients were grouped into two groups (unilateral, 14; bilateral, 6) according to disease severity. The results showed no significant differences in postural sway variability between the groups (p >= 0.05). Postural sway variability was higher in the antero-posterior direction and with the eyes closed. Significant differences between the unilateral and bilateral groups were observed in clinical tests (UPDRS, Berg Balance Scale, and retropulsion test; p <= 0.05, all). Postural sway variability was unaffected by disease severity, indicating that neurological mechanisms for postural control still function at advanced stages of disease. Postural sway instability appears to occur in the antero-posterior direction to compensate for the stooped posture. The eyes-closed condition during upright stance appears to be challenging for PD patients because of the associated sensory integration deficit. Finally, objective measures such as postural sway variability may be more reliable than clinical tests to evaluate changes in balance control in PD patients.
Keywords: variability, postural control, sensory information, balance tests.
RESUMO
Variabilidade de oscilação postural, testes de equilíbrio de Berg e retropulsão foram investigados em pacientes com DP em diferentes estágios da doença. Vinte pacientes com DP participaram deste estudo e foram distribuídos em dois grupos: unilateral (14) e bilateral (6). Os resultados mostraram diferença não significativa entre os grupos para a variabilidade de oscilação postural (p>=0.05). Ainda, a variabilidade de oscilação postural foi maior na direção antero-posterior e na condição de olhos fechados. Para os testes clínicos, UPDRS (seções funcional e motora), teste de Berg e retropulsão, foi encontrada diferença significativa entre os grupos (unilateral e bilateral) (p<=0.05). A partir destes resultados, foi possível concluir que a variabilidade de oscilação postural não muda em função da severidade da doença. Os mecanismos neurológicos para o controle postural ainda estão operando no estágio avançado da doença. Assim, a instabilidade postural parece ocorrer na direção antero-posterior como um mecanismo compensatório em função da postura rígida. A condição de olhos fechados parece ser desafiadora para pacientes com DP, em função dos deficits da integração sensorial. Finalmente, a variabilidade de oscilação postural pode ser considerada uma medida confiável, pois elimina o efeito da subjetividade.
Palavras-chave: variabilidade, controle postural, informação sensorial, testes de equilíbrio.
INTRODUCTION
Postural instability is characterized by increased body sway during quiet stance as a result of impaired postural control. Postural instability is a major disabling feature in Parkinsons disease (PD) patients and a primary risk factor for falls. Postural instability has been reported in 68% of PD patients (Ashburn, Stack, Pickering, & Ward, 2001). Postural sway is greater in the anterior-posterior and medial-lateral directions in patients with PD than in healthy old adults, which is attributed to a progressive decline in postural stability control (Janusz W. Błaszczyk & Orawiec, 2011). Additionally, greater postural impairment during sensory manipulation tasks (eyes closed and changing visual information) has been observed in patients with PD than in healthy controls, suggesting that basal ganglia are crucial for sensory-motor integration (Brown et al., 2006; Suarez et al., 2011). Moreover, patients with PD are highly visually dependent and continue to use visual cues for postural control even when information is not appropriate (Azulay et al., 1999). In fact, Błaszczyk, Orawiec, Duda-Kłodowska, and Opala, (2007) found higher medial-lateral sway in the eyes-closed than in the eyes-open condition in PD patients compared to healthy controls and concluded that PD patients have postural instability in challenging visual conditions (eyes closed), suggesting that the eyes-closed condition may be associated with a higher risk for falls.
Patients at more advanced stages of PD have postural instability as evidenced by a re-tropulsion test (Item 30 of the Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale – UPDRS) (Fahn & Elton, 1986). Frenklach, Louie, Koop, and Bronte-Stewart (2009) investigated postural sway in static (still platform) and dynamic (sway referenced platform) conditions and found excessive postural sway at more advanced stages of the disease, suggesting that patients in later stages of PD are at an increased risk for falling. Thus, investigating postural control at different stages of the disease may help identify the risk for falling and sensory-motor problems to initiate a postural rehabilitation program in PD patients.
Postural instability in PD patients can be evaluated by measuring the center of pressure (Błaszczyk et al., 2007; Matinolli et al., 2007), postural sway angle (Adkin, Bloem, & Allum, 2005), and trunk linear acceleration (Mancini et al., 2012). Although these postural sway analyses quantify changes in postural control, they do not assess postural sway variability due to disease progression in different visual conditions (eyes open and closed) and postural sway directions (anterior-posterior and medial-lateral). Postural sway variability may help identify disabling features of the disease such as postural instability and changes in the behaviour of PD patients due to disease progression (van Emmerik & van Wegen, 2002) and play a functional role by helping explore and identify stability boundaries in these patients. In addition, postural sway variability may also help identify changes in postural control in PD patients at different stages of disease and in different visual conditions. Moreover, postural sway variability may also be used in postural control studies to detect postural instability in different visual conditions and postural sway directions.
Some clinical tests such as the retropulsion test (Item 30/UPDRS) and the Berg Balance Scale (BBS) have also been used to identify changes in postural control in PD patients (Jenkins, Johnson, Holmes, Stephenson, & Spaulding, 2010). However, these clinical tests are subjective, indirect measures of postural control. Moreover, it is not known whether the same changes in PD postural control due to disease progression may be identified in postural sway variability (direct measure) and in clinical tests (indirect measure). This study aimed to investigate postural sway variability in PD patients at different stages of disease in different visual conditions (eyes open and closed) and postural directions (anterior-posterior and medial-lateral) and compare the postural control performance of PD patients in clinical (Item 30), functional (BBS), and postural sway variability tests.
METHODS
Participants
Twenty patients with idiopathic PD ranging from 1 to 3 on the Hoehn and Yahr (HY) scale (Hoehn & Yahr, 1967) participated in this study. Participants were grouped into two HY groups according to severity of PD: unilateral (stages 1 and 1.5) and bilateral (stages 2–3) disease. The inclusion criteria were: diagnosis of PD and absence of neuromuscular, vestibular, or osteoarticular disorders and dementia, which could affect postural task performance. All participants followed their usual medication regimen during testing. The study was approved by the local ethics committee (UNESP/RC). All participants signed an informed consent form.
Procedures
Data were collected on two consecutive days. On the first day, the demographic, anthropometric, and clinical variables including PD severity (HY and UPDRS staging) and cognitive screening (Mini-Mental State Exam – MMSE) were determined. The Berg Balance Scale (BBS), which includes 14 items that evaluate the ability to maintain balance in different postural positions, was applied to measure functional balance, whereas the UPDRS retropulsion test (Item 30 – motor section) is a clinical test that was used to determine postural stability in PD patients. Higher scores in the BBS and retropulsion tests indicate better and worse performance, respectively.
On the second day, postural instability was determined using postural sway kinematic analysis. Participants were asked to wear reflective markers and postural tasks were recorded with a digital camcorder. The postural task consisted of standing as quietly as possible for 30 sec with eyes open (EO) and eyes closed (EC). Participants wore goggles in the eyes-closed condition to ensure that no visual information was captured. Three 30-sec trials were performed in each condition and trials were randomized.
Postural sway was assessed in the medial-lateral (ML) and anterior-posterior (AP) directions and recorded with a digital camcorder with a 60 Hz field rate that created 2D kinematic data. Fifteen-mm reflective markers were placed on the right and left acromion process and right and left anterior center of the ankle joint for the ML analysis and on the right acromion and right lateral malleolus for the AP analysis, totalling six reflective markers. These anatomical landmark positions are based on an inverted pendulum model and are appropriate for measuring postural instability (Suarez et al., 2011).
The measuring area was calibrated prior to each postural task analysis. Images were captured by a video card coupled to a computer. Markers were digitized automatically using the Digital Video for Windows (DVIDEOW) software (Figueroa, Leite, & Barros, 2003). The x and y coordinates for each marker were converted to the metric system using a bidimensional reference system with four control points (1.5 x 1.8 m). Raw data were filtered using a low-pass, second-order digital Butterworth filter with a cut-off frequency of 5 Hz using the Matlab 7® software.
Statistical Analysis
The score of each item was computed for the BBS and UPDRS (Item 30) analyses. The angular amplitude of body oscillation (degrees), used as the dependent variable, was calculated by subtracting the maximum and minimum body oscillation values during the entire trial in both directions (anterior-posterior and medial-lateral). Postural sway variability was determined by calculating the standard deviation of the angular amplitude oscillation.
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Levene tests showed that the data were not normally distributed and homogenous and thus the unpaired Mann-Whitney test was used to compare differences in group characteristics and clinical balance tests between the HY groups. Because postural sway variables were normally distributed (Kolmogorov-Smirnov test) and homogenous (Levene test), we used a three-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with repeated measures to compare postural sway variability between HY groups (unilateral and bilateral), conditions (eyes open and closed), and direction (AP and ML). The cut-off criteria for the effect size (partial eta squared [ηp2]) were: small effect (0.20 <= ηp2 < 0.50), medium effect (0.50 <= ηp2 < 0.80), and large effect (ηp2 >= 0.80) as suggested by Cohen (1992). The observer power (0–1) was also analysed. The significance level was set at p <= 0.05. All analyses were performed using the SPSS software (SPSS for Windows 10.0®).
RESULTS
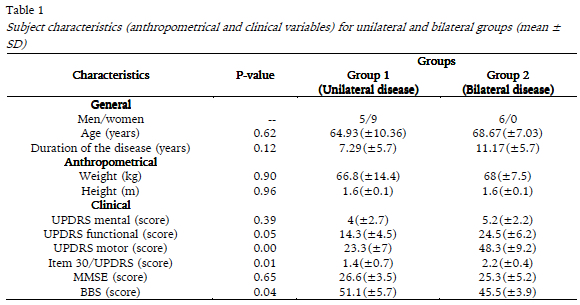
There were no differences in age, height, weight, disease duration, cognitive state (MMSE), and UPDRS staging (mental section) between the unilateral and bilateral groups. However, the motor and functional UPDRS scores were significantly lower in the unilateral group than in the bilateral group, whereas the opposite result was observed in the BBS score (Mann-Whitney test, p <= 0.05 all; Table 1).
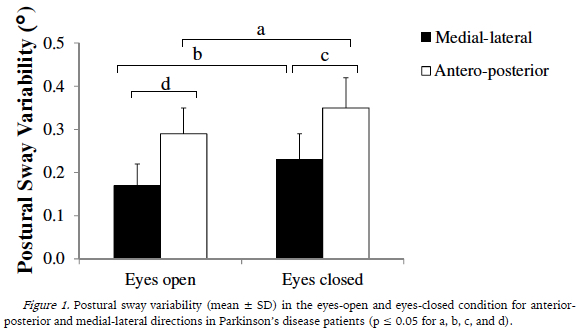
The three-way ANOVA (HY group x eye condition x sway direction) with repeated measures on the last two factors showed no significant differences between HY groups (F1,18 = 34.02, p = 0.86, ηp2 = 0.65, observer power = 1.0) and interaction (F1,18 = 1.48, p = 0.24, ηp2 = 0.076, observed power = 0.73), but showed significant differences in eye condition (F1,18 = 7.35, p = 0.014, partial ηp2 = 0.29, observed power = 0.74) and sway direction (F1,18 = 11.42, p = 0.003, ηp2 = 0.38, observed power = 0.89). Postural sway variability in the AP and ML directions was greater in the eyes-closed than in the eyes-open condition for both groups (Figure 1). In addition, postural sway variability was higher in the AP than in the ML direction for both visual conditions (Figure 1).
DISCUSSION
This study aimed to evaluate postural sway variability and postural control performance in different balance tests (Item 30, BBS, and upright stance) in PD patients at different stages of disease. Postural sway variability was not affected by disease severity. In addition, postural control mechanism was preserved during the static upright stance task in patients at moderate stages of disease. Thus, balance control mechanisms are likely still operative in PD patients at moderate stages of disease.
Frenklach et al. (2009) evaluated postural sway in patients with PD at different stages of disease and healthy controls under static and dynamic conditions with eyes open, eyes closed, and sway-referenced visual surround (sensory organization test). The authors did not find any differences between patients at early stages of PD and healthy controls for all sensory conditions tested. However, they showed that postural sway increased with disease severity. The contrasting results between that study and ours may be explained by the medication status of participants: patients were evaluated off dopaminergic medication in Frenklach et al. (2009), whereas in our study participants were evaluated while taking their current medication. In fact, stability limits are influenced by the levodopa status in patients with PD (Mancini, Rocchi, Horak, & Chiari, 2008). Moreover, we investigated PD patients at early and moderate stages of disease, whereas Frenklach et al. (2009) evaluated PD patients at advanced stages. Thus, the different results observed between Frenklach et al. (2009) and our study may be explained by the different medication status and disease severity. Moreover, even though we did not include healthy controls in our study, no significant differences in any stabilographic parameters have been observed in results published elsewhere between healthy controls and people with PD at early and moderate stages (Zawadka-Kunikowska et al., 2014).
No patients in this study presented dyskinesia or motor fluctuations that could compromise balance in postural tasks (Armand, Landis, Sztajzel, & Burkhard, 2009). Chastan, Debono, Maltête, and Weber (2008) observed some changes in dynamic postural conditions between patients at early stages of PD and healthy subjects. Despite the changes in postural stability, patients at early stages of PD were also able to recover balance during dynamic tasks, as were healthy subjects. We could also have investigated postural sway variability in more threatening tasks and some differences between PD patients and healthy adults may have been observed.
We found increased postural sway variability not only in the antero-posterior direction, but also in the eyes-closed condition. Thus, we can conclude that postural sway instability occurs in the antero-posterior direction and eyes-closed condition, because postural sway variability was higher in these two conditions. The eyes-closed condition is considered a challenging task that disturbs postural sway in PD patients. Brown et al. (2006) observed increased postural sway in static conditions with eyes closed and showed that it took more time for PD patients than for healthy controls to stabilize upright stance after vision was restored. Recently, Oude Nijhuis, Allum, Nanhoe-Mahabier, and Bloem (2014) have shown that center of mass displacement was 17% greater in the eyes-closed than in the eyes-open condition in PD patients. In our study, we also show that the eyes-closed condition is more threatening for PD patients, because it increases postural sway variability. Thus, increased postural sway variability can be described as a change in the postural control system caused by PD and may be an impaired compensatory mechanism for recovering balance. Moreover, the increased postural sway variability may stem from a deficit in the reorganization of sensory information for postural control, indicating that basal ganglia are critical for integrating sensory information (Brown et al., 2006). The increased body sway in the antero-posterior direction observed in our study represents an impairment of the postural system and may be associated with falls.
We also observed that PD patients adopted a stooped posture in the UPDRS test. The stooped posture is characterized by forward tilting of the center of mass and is a compensatory posture used to fight instability that may be partly responsible for the abnormal postural responses in subjects with PD (Jacobs, Dimitrova, Nutt, & Horak, 2005). Thus, the increased postural variability in the antero-posterior direction may be a compensatory mechanism for the stooped posture (Benatru, Vaugoyeau, & Azulay, 2008). The results of this study are in agreement with other studies that reported increased postural sway in the anterior-posterior direction (Błaszczyk et al., 2007) in the eyes-closed condition. Because of the rigidity and functionality problems observed in the UPDRS test, PD patients were not able to compensate for the postural sway in the medial-lateral direction, resulting in greater postural instability in the antero-posterior direction. Thus, the increased postural sway variability in the anterior-posterior direction is a compensatory mechanism for postural sway that occurs in the same direction as the postural problems (Benatru et al., 2008), as well as for cervical rigidity (Franzén et al., 2009). Cervical rigidity plays a significant role in functional mobility and may contribute significantly to balance and mobility disorders (Franzén et al., 2009). It should be noted that the UPDRS test is limited by the subjective estimation of tone in the extremities and the neck when the patient is sitting.
The differences in UPDRS II-III scores between the HY groups were expected, because of the difference in disease severity between the unilateral and bilateral groups. Similarly, performance in the BBS and Item 30 test was also affected by disease severity: patients in the unilateral group performed better than patients in the bilateral group. This result is in agreement with Hoehn and Yahr (1967), who showed postural instability in PD patients at moderate and severe stages of disease. However, postural sway variability was not affected by disease progression in our study. Thus, postural sway variability may be more reliable than clinical tests to identify factors that affect balance control in PD patients, because it is an objective measure that recognizes changes in body balance with aging and neurological disease (van Emmerik & van Wegen, 2002). Based on these results, we suggest that postural sway variability rather than indirect tests such as the BBS and retropulsion test can be used in clinical practice to evaluate body balance control because this variable can detect significant changes in postural control.
The type of task used in each clinical test should also be considered, because the upright stance task is a static test whereas the BBS and Item 30 include dynamic tasks. Previously, Jenkins, Johnson, Holmes, Stephenson, and Spaulding (2010) also reported that the UPDRS test may not be appropriate to evaluate postural stability in PD patients. In that study, the authors found that a functional reaching test is more reliable to evaluate postural instability. Moreover, the level of difficulty of each test should also be considered. For instance, the upright stance task is not threatening for PD patients at any stage of disease, whereas the clinical balance tests may be more challenging because of the dynamic tasks. Additionally, for patients at more advanced stages of PD the dynamic tasks might be more difficult to perform. Lastly, dual-task paradigms and dynamic tasks may also be used to identify functional changes in postural control as a result of disease progression.
One limitation of this study is that we did not include a healthy control group and more advanced stages of PD that could provide additional evidence about postural sway variability during disease progression. Additionally, we used a single segment (inverted pendulum) to analyze postural control. Analyzing quiet stance in different body strategies could have also been beneficial because the postural control system is more complex than an inverted pendulum and behaves like a multilink pendulum (Creath, Kiemel, Horak, Peterka, & Jeka, 2005). Although postural control should be analyzed as a multilink pendulum, it has been shown that PD patients do not use a hip strategy, because they have small responses, stiff postural coordination, and impaired proprioception (Baston, Mancini, Schoneburg, Horak, & Rocchi, 2014). Thus, the placement of reflective markers on the shoulder and the ankle was appropriate to quantify postural sway variability as an inverted pendulum (Suarez et al., 2011).
CONCLUSION
Postural sway variability was not affected by disease severity and was in the anterior-posterior direction, likely to compensate for the stooped posture. In addition, postural sway variability was higher in the eyes-closed condition, which appears to be challenging for PD patients because of the associated sensory integration deficit. Finally, clinical tests and postural sway variability differed in their ability to detect postural changes in PD patients. We suggest that objective measures such as postural sway variability may be used in clinical practice to evaluate changes in balance control in PD patients.
REFERÊNCIAS
Adkin, A. L., Bloem, B. R., & Allum, J. H. J. (2005). Trunk sway measurements during stance and gait tasks in Parkinsons disease. Gait & Posture, 22(3), 240–249. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2004.09.009 [ Links ]
Armand, S., Landis, T., Sztajzel, R., & Burkhard, P. R. (2009). Dyskinesia-induced postural instability in Parkinsons disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 15(5), 359–364. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.08.007 [ Links ]
Ashburn, A., Stack, E., Pickering, R. M., & Ward, C. D. (2001). A community‐dwelling sample of people with Parkinsons disease: characteristics of fallers and non‐fallers. Age and Ageing, 30(1), 47–52. http://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/30.1.47 [ Links ]
Azulay, J.-P., Mesure, S., Amblard, B., Blin, O., Sangla, I., & Pouget, J. (1999). Visual control of locomotion in Parkinsons disease. Brain, 122(1), 111–120. http://doi.org/10.1093/brain/122.1.111 [ Links ]
Baston, C., Mancini, M., Schoneburg, B., Horak, F., & Rocchi, L. (2014). Postural strategies assessed with inertial sensors in healthy and parkinsonian subjects. Gait & Posture, 40(1), 70–75. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2014.02.012 [ Links ]
Benatru, I., Vaugoyeau, M., & Azulay, J.-P. (2008). Postural disorders in Parkinsons disease. Clinical Neurophysiology, 38(6), 459–465. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2008.07.006 [ Links ]
Błaszczyk, J. W., & Orawiec, R. (2011). Assessment of postural control in patients with Parkinsons disease: Sway ratio analysis. Human Movement Science, 30(2), 396–404. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2010.07.017 [ Links ]
Błaszczyk, J. W., Orawiec, R., Duda-Kłodowska, D., & Opala, G. (2007). Assessment of postural instability in patients with Parkinsons disease. Experimental Brain Research, 183(1), 107–114. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1024-y [ Links ]
Brown, L. A., Cooper, S. A., Doan, J. B., Clark Dickin, D., Whishaw, I. Q., Pellis, S. M., & Suchowersky, O. (2006). Parkinsonian deficits in sensory integration for postural control: Temporal response to changes in visual input. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 12(6), 376–381. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2006.03.004 [ Links ]
Chastan, N., Debono, B., Maltête, D., & Weber, J. (2008). Discordance between measured postural instability and absence of clinical symptoms in Parkinsons disease patients in the early stages of the disease. Movement Disorders, 23(3), 366–372. http://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21840 [ Links ]
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 155–159. http://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.155 [ Links ]
Creath, R., Kiemel, T., Horak, F., Peterka, R., & Jeka, J. (2005). A unified view of quiet and perturbed stance: simultaneous co-existing excitable modes. Neuroscience Letters, 377(2), 75–80. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.11.071 [ Links ]
Fahn, S., & Elton, R. (1986). Unified Parkinsons disease rating scale. Em S. Fahn, P. Jenner, C. D. Marsden, & P. Teychenne (Eds.), Recent Developments in Parkinsons Disease (pp. 153– 163). Londres: Macmillan. [ Links ]
Figueroa, P. J., Leite, N. J., & Barros, R. M. L. (2003). A flexible software for tracking of markers used in human motion analysis. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 72(2), 155–165. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-2607(02)00122-0 [ Links ]
Franzén, E., Paquette, C., Gurfinkel, V. S., Cordo, P. J., Nutt, J. G., & Horak, F. B. (2009). Reduced performance in balance, walking and turning tasks is associated with increased neck tone in Parkinsons disease. Experimental Neurology, 219(2), 430–438. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.06.013 [ Links ]
Frenklach, A., Louie, S., Koop, M. M., & Bronte-Stewart, H. (2009). Excessive postural sway and the risk of falls at different stages of Parkinsons disease. Movement Disorders, 24(3), 377–385. http://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22358 [ Links ]
Hoehn, M. M., & Yahr, M. D. (1967). Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology, 17(5), 427–442. [ Links ]
Jacobs, J. V., Dimitrova, D. M., Nutt, J. G., & Horak, F. B. (2005). Can stooped posture explain multidirectional postural instability in patients with Parkinsons disease? Experimental brain research. Experimentelle Hirnforschung. Experimentation cerebrale, 166(1), 78–88. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-2346-2 [ Links ]
Jenkins, M. E., Johnson, A. M., Holmes, J. D., Stephenson, F. F., & Spaulding, S. J. (2010). Predictive validity of the UPDRS postural stability score and the Functional Reach Test, when compared with ecologically valid reaching tasks. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 16(6), 409–411. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2010.04.002 [ Links ]
Mancini, M., Carlson-Kuhta, P., Zampieri, C., Nutt, J. G., Chiari, L., & Horak, F. B. (2012). Postural sway as a marker of progression in Parkinsons disease: A pilot longitudinal study. Gait & Posture, 36(3), 471–476. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2012.04.010 [ Links ]
Mancini, M., Rocchi, L., Horak, F. B., & Chiari, L. (2008). Effects of Parkinsons disease and levodopa on functional limits of stability. Clinical Biomechanics, 23(4), 450–458. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2007.11.007 [ Links ]
Matinolli, M., Korpelainen, J. T., Korpelainen, R., Sotaniemi, K. A., Virranniemi, M., & Myllylä, V. V. (2007). Postural sway and falls in Parkinsons disease: A regression approach. Movement Disorders, 22(13), 1927–1935. http://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21633 [ Links ]
Oude Nijhuis, L. B., Allum, J. H. J., Nanhoe-Mahabier, W., & Bloem, B. R. (2014). Influence of Perturbation Velocity on Balance Control in Parkinsons Disease. PLoS ONE, 9(1), e86650. http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0086650 [ Links ]
Suarez, H., Geisinger, D., Ferreira, E. D., Nogueira, S., Arocena, S., Roman, C. S., & Suarez, A. (2011). Balance in Parkinsons disease patients changing the visual input. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, 77(5), 651–655. http://doi.org/10.1590/S1808-86942011000500019 [ Links ]
Van Emmerik, R. E. A., & van Wegen, E. E. H. (2002). On the functional aspects of variability in postural control. Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews, 30(4), 177–183. http://doi.org/10.1097/00003677-200210000-00007 [ Links ]
Zawadka-Kunikowska, M., Zalewski, P., Klawe, J. J., Pawlak, J., Tafil-Klawe, M., Kędziora-Kornatowska, K., & Newton, J. L. (2014). Age-related changes in cognitive function and postural control in Parkinsons disease. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research, 26(5), 505–510. http://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-014-0209-z [ Links ]
Acknowledgments:
Nothing to declare.
Conflicts of Interest:
Nothing to declare.
Funding:
Nothing to declare.
Manuscript received January 20th, 2014; Accepted May 27th, 2014
* Autor correspondente: Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto – USP, Av. Bandeirantes, 3900 – Ribeirão Preto – SP. 14040-907; E-mail: narinaldi@yahoo.com.br